1. Intramuscular (IM) Injection
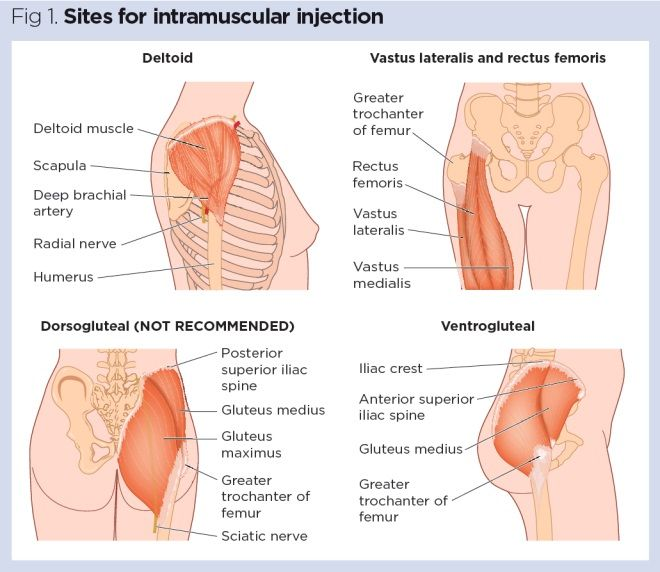
– Injected into the muscle tissue, allowing for slow and sustained release of medication.
– Commonly used for medications that require gradual absorption or for large volumes of medication.
– Examples include vaccines, certain antibiotics, and some hormones.
2. Intravenous (IV) Injection
3. Subcutaneous (SC) Injection
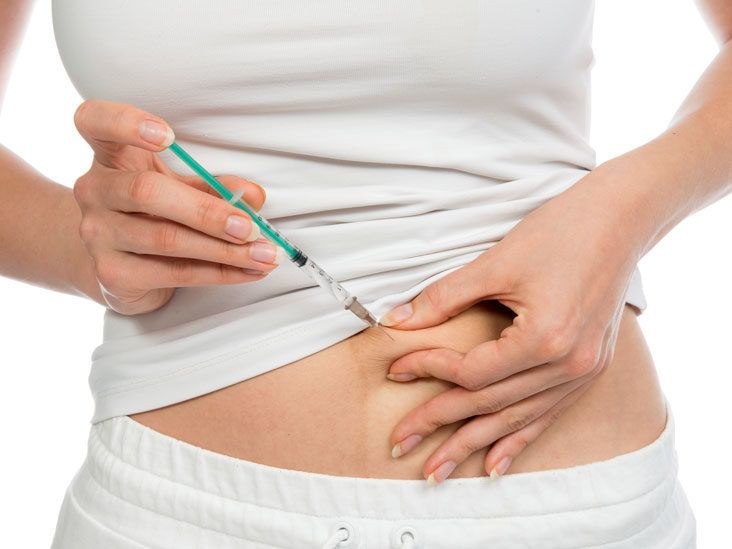
– Injected beneath the skin into the fatty tissue layer.
– Allows for slow and steady absorption of medication into the bloodstream.
– Used for medications that require sustained release or for small volumes of medication.
– Examples include insulin, certain vaccines, and some hormones.
4. Intradermal (ID) Injection
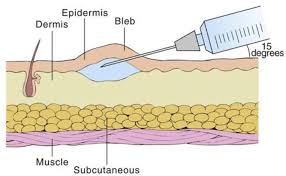
– Injected into the dermis layer of the skin.
– Used for diagnostic purposes (e.g., skin testing for allergies) or for administration of certain vaccines (e.g., tuberculosis test).
5. Intraosseous (IO) Injection
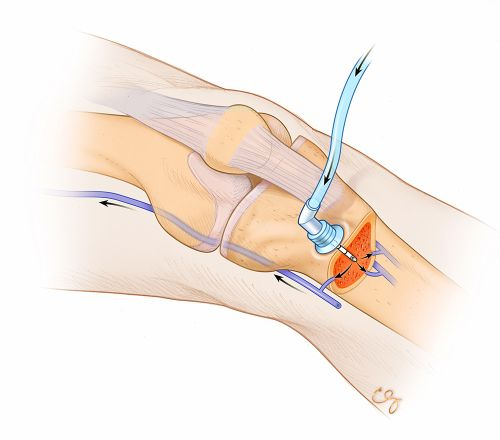
– Administered directly into the bone marrow.
– Used in emergency situations when intravenous access is difficult or not feasible.
Parenteral injections are essential in medical practice for delivering medications, fluids, and nutrients directly into the body. They are administered by trained healthcare professionals to ensure safety and effectiveness. Proper technique, sterile equipment, and careful monitoring are crucial to minimize complications and maximize therapeutic benefits.
